¿Qué es un Predicado?
Brian wants to add a discussion of domain and range to this part of the course. --MF, 12/16/18
This page has been restructured yet again.
Need to check solution files (including numbering and note on problem 2). --MF, 8/8/19
En este laboratorio, tú vas a desarrollar herramientas que ayudarán a resolver una sopa de letras mediante la búsqeuda de palabras que cumplan con ciertas características.
En esta página, tú vas a revisar predicados y construir algunos que podrás utilizar en otros proyectos.
As you know, predicates are reporter blocks (functions) that always report a Boolean value (they report only the values  or
or  ). In Snap!, predicates are represented by hexagonal blocks. They compute the condition used by conditionals (such as
). In Snap!, predicates are represented by hexagonal blocks. They compute the condition used by conditionals (such as if, if else, or repeat until) to decide when to do something. Predicates ask a question such as "Is the random number 3?" or "Is this sprite touching the sprite called 'Leader'?"
Every if else block has two scripts inside of it, exactly one of which will be run depending on the value that the predicate reports. Then the computer continues with whatever comes after the if else block.

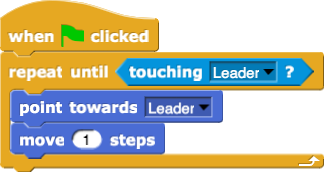
You may see these five relational operators:
=, >, <, ≥, ≤
as well as a sixth:
≠
, which means "not-equal" and reports
false if the two inputs are equal and otherwise reports
true (if they are not equal). When you write the

block, it will work like this:


These six relational operators all report a Boolean value (true or false).
-
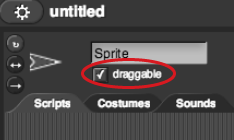 Make the sprite draw only if the mouse button is down, so that you can draw disconnected shapes. You'll need to uncheck the "draggable" box above the scripting area (shown right) before you try this (so that Snap! doesn't think you are trying to drag the sprite when you click).
Make the sprite draw only if the mouse button is down, so that you can draw disconnected shapes. You'll need to uncheck the "draggable" box above the scripting area (shown right) before you try this (so that Snap! doesn't think you are trying to drag the sprite when you click).
You'll probably want to use the

block, which you can find in the Sensing palette.
:
Selection
Selection means deciding (selecting) which part of an algorithm to run based on whether a condition is true or false.
Every algorithm can be constructed using sequencing (following steps in order), selection (deciding), and iteration (repeating).
 or
or  ). In Snap!, predicates are represented by hexagonal blocks. They compute the condition used by conditionals (such as
). In Snap!, predicates are represented by hexagonal blocks. They compute the condition used by conditionals (such as 



 block, it will work like this:
block, it will work like this:

 Make the sprite draw only if the mouse button is down, so that you can draw disconnected shapes. You'll need to uncheck the "draggable" box above the scripting area (shown right) before you try this (so that Snap! doesn't think you are trying to drag the sprite when you click).
Make the sprite draw only if the mouse button is down, so that you can draw disconnected shapes. You'll need to uncheck the "draggable" box above the scripting area (shown right) before you try this (so that Snap! doesn't think you are trying to drag the sprite when you click). block, which you can find in the Sensing palette.
block, which you can find in the Sensing palette.